- Home
- Health Center
- Health Info
- The Difference Between Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes
Heart
The Difference Between Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes
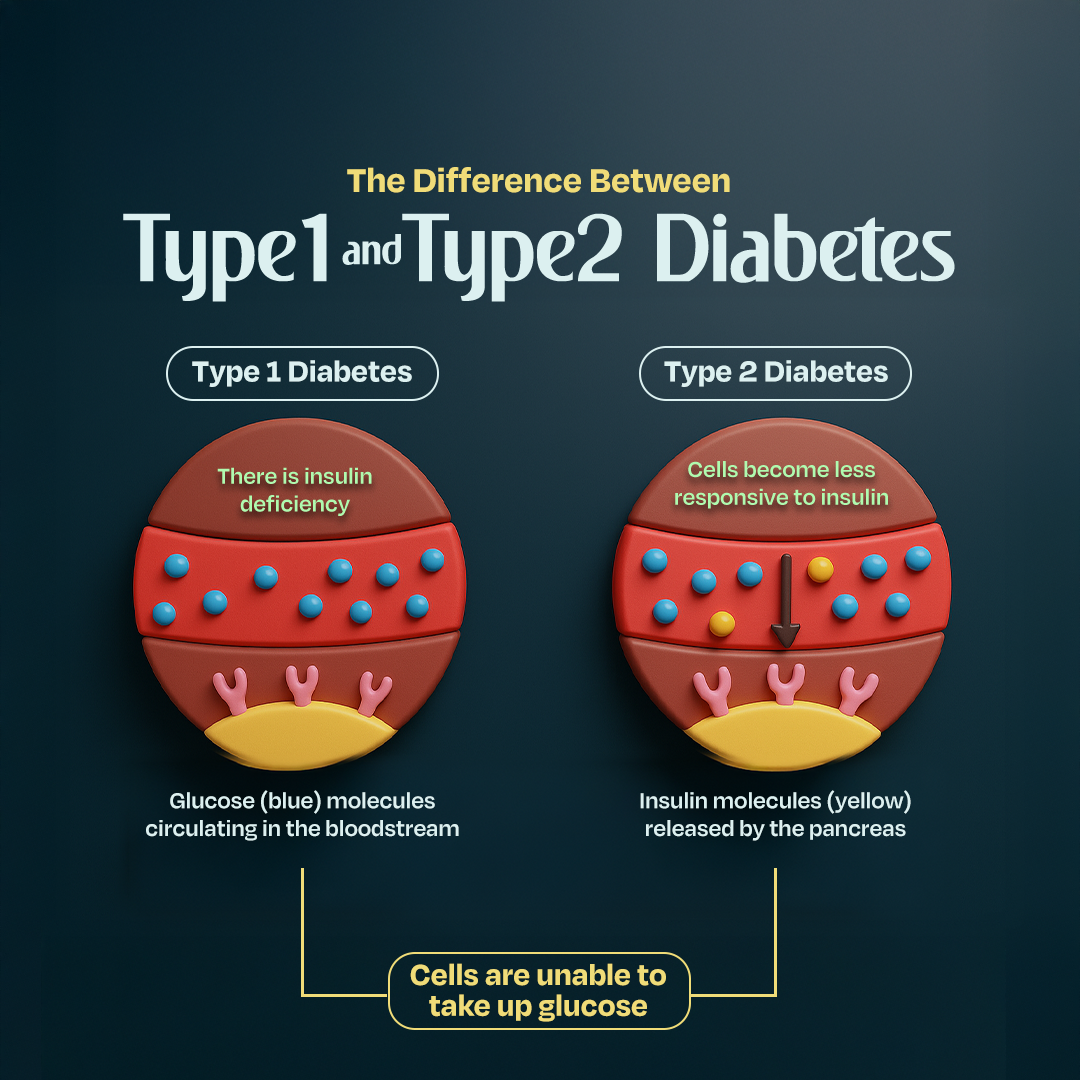

Type 1 vs Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus – What’s the difference?
Diabetes mellitus is often perceived as a single condition; however, the reality is that Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes are both different diseases with unique causes, risk factors, and management needs. In this article, we will discuss and provide a clear comparison of Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes, similarities in their signs and symptoms, and their management.
Comparison between Type 1 & Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
The key differences between type 1 and type 2 diabetes include a few features such as age of onset, pathogenesis (progression of condition), insulin dependency and prevalence. This can be concluded by referring to the table below.
Type 1 DM (¹⸴²) | Type 2 DM (³⸴⁴) | |
Pathogenesis (Progression of Condition) | Autoimmune disorder which is characterised by the loss of insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. The loss is mediated by the immune system where the beta cells are mistakenly identified as foreign cells and attacked (this leads to insulin deficiency). | Primarily characterised by insulin resistance, where the body’s cells become less responsive to insulin, combined with insulin deficiency. However, over time, the pancreas is unable to maintain this, leading to a gradual decline in insulin secretion. |
Age of onset | Childhood or adolescence | Usually in adults, especially above 40 years of age |
Insulin dependence | Always requires insulin | Initially might not need insulin |
Prevalence | Less common (~ 5-10% of people with diabetes) | More common (~90-95% of people with diabetes) |
Similarities in Signs & Symptoms
Despite their distinct progression, there are a few common similarities shared by Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus which include insulin resistance, consistently elevated blood sugar levels and their impact on the nerves, eyes and cardiovascular system.(¹⸴²)
Both conditions may also result in clinical symptoms like: (²)
– Polyuria (Excessive or frequent urination)
– Polydipsia (Excessive thirst)
– Polyphagia (Excessive hunger)
Management of Type 1 & Type 2 (⁵⸴⁶)
The management of Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus can differ in treatment. While insulin therapy is essential to Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus due to the body producing little to no insulin, those who have Type 2 may only need insulin in later stages of their condition. Besides that, lifestyle modification such as nutrition monitoring and exercise can also improve blood glucose in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. For patients who are on insulin, it is essential to do self monitoring of blood glucose at home, remember sick day management and to watch for symptoms of low blood sugar.
For more information on Type 1 or Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, visit your nearest CARiNG Pharmacy outlet and ask your friendly Pharmacist!
REFERENCES:
- Atkinson MA, Eisenbarth GS. Type 1 diabetes: New perspectives on disease pathogenesis and treatment. Lancet. 2001;358(9277):221-9. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(01)05395-3
- American Diabetes Association. Classification and diagnosis of diabetes: Standards of medical care in diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2020;43(Suppl 1):S14-31. doi: 10.2337/dc20-S002
- Kahn SE, Haffner SM. Type 2 diabetes mellitus. Lancet. 2008;371(9623):1229-40. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(08)60435-8
- Zimmet P, Alberti KG, Shaw J. Global and societal implications of the diabetes epidemic. Nature. 2001;414(6865):782-7. doi: 10.1038/
- Ministry of Health Malaysia. Clinical Practice Guidelines: Management of Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus in Children and Adolescents. Putrajaya: Ministry of Health Malaysia; 2015.
- Ministry of Health Malaysia. Clinical Practice Guidelines: Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. 6th ed. Putrajaya: Ministry of Health Malaysia; 2020.
Tags
Latest Health Info
Brave the Cold: Winter Travel Needs
Winter travel has its kind of magic — snow-covered landscapes, cozy lodges, hot drinks, and festive markets. But traveling in ...
Beat the Heat When Travelling
Whether you’re on a scenic beach vacation or exploring a busy city, hot weather can quickly wear you out and ...
Got Pins & Needles? Learning about Diabetic Neuropathy
Diabetic neuropathy is a common yet serious complication of diabetes, estimated to affect up to 50% of people with the ...



